Browser Grid Features
This section explores the various features that make up the Browser Grid component.
Hub
Hub is a virtual machine that acts as a controller. When a user sends requests to the headless browser present in a browser grid, the Hub will allot a node to run the headless browser to execute the request. The functionality of the Hub is entirely handled by the Catalyst SmartBrowz service. This ensures your grid can scale seamlessly to handle your request load.
Nodes
Nodes are virtual machines that run the required headless browsers. Based on the configuration, you can dictate the number of nodes that need to be created in your browser grid and the number of headless browsers that need to be spawned in each node.
-
The default allocated storage limit is 10GB.
Headless Browsers
Headless browsers are browsers that run without a Graphical User Interface (GUI). These types of browsers are the entities or instances that execute and process the requests sent by the user.
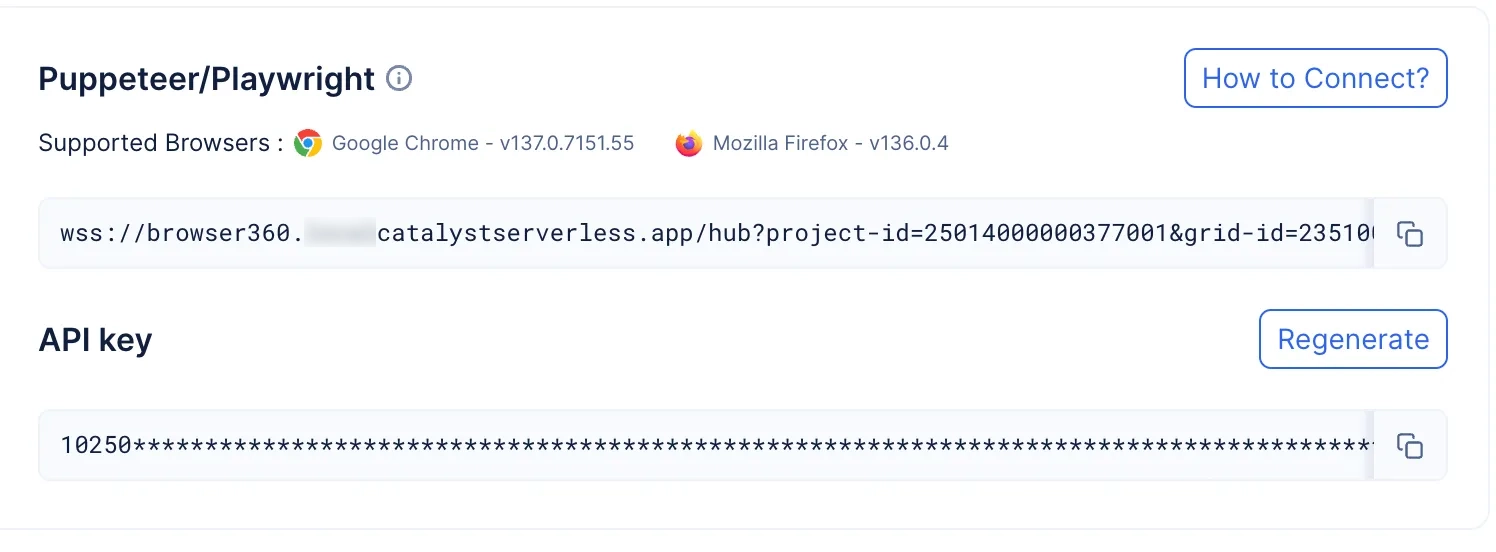
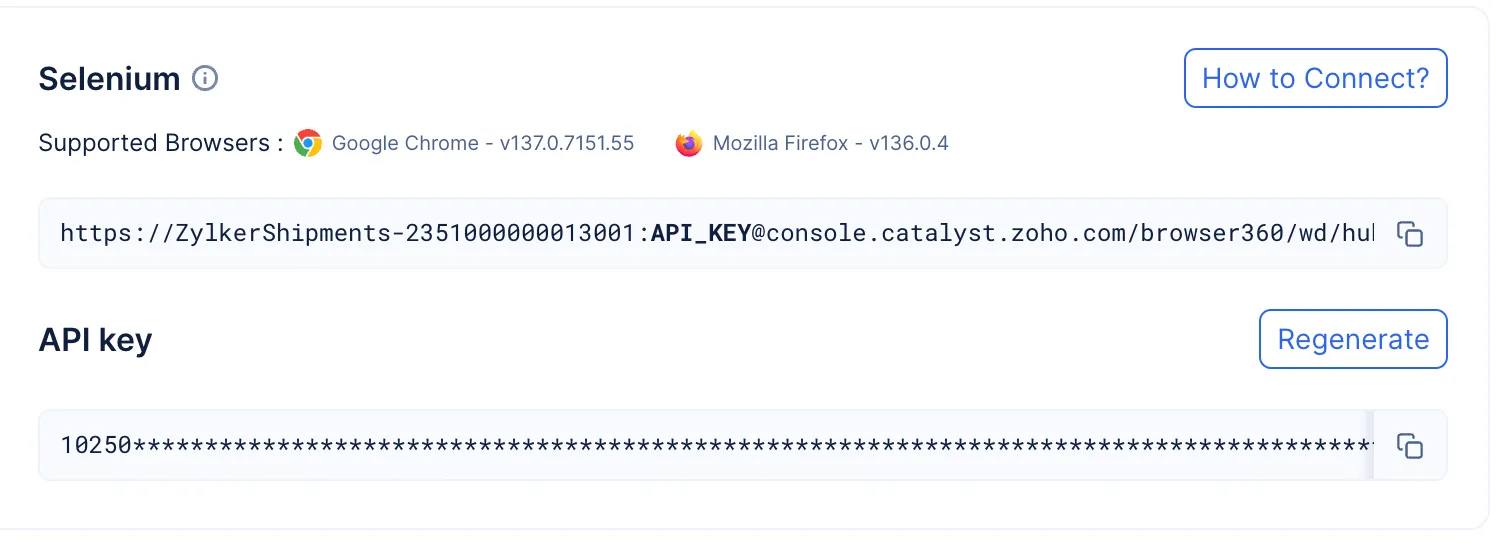
The Browser Grid component provides you with the option to effortlessly connect to multiple secure remote browsers using popular automation libraries like Puppeteer, Playwright, and Selenium.
Based on your requirement, you have the option to choose your automation library and launch your required secure headless browser using a CDP/Webdriver endpoint generated by the Catalyst SmartBrowz service.
The endpoint is made secure using an API KEY which will be uniquely generated for you.
- Learn the steps to process your requests through a headless browser.
- While you do have the option to change the automation library you use to connect to your headless browser, you do not have the option to use multiple automation libraries within the same browser grid simultaneously.
Browser Grid Configuration
In a browser grid, you can define the number of nodes and the number of browsers that can be created in a singular node. The configuration also allows you to set the number of browsers that can be run concurrently. When you create or update an existing grid, you have the option to choose:
- Basic Configuration: This is a type of configuration that is best suited to handle an ideal load of requests, with a processing power of 1GiB Memory, 1vCPU.
- Advanced Configuration: This type of configuration allows you the option to choose the number of nodes and the number of browsers allotted per node. You will have the following options:
- Light Node Type: You can choose to create a Grid that has a processing power of 1GiB Memory, 1vCPU.
- Moderate Node Type: You can choose to create a Grid that has a processing power of 2GiB Memory, 2vCPU.
- Heavy Node Type: You can choose to create a Grid that has a processing power of 4GiB Memory, 4vCPU.
The following table will further detail the differences between the various configurations:
| Category | Basic Configuration | Advanced Configuration | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light | Moderate | Heavy | ||
| Node Type | Light - 1GiB Memory, 1vCPU | 1GiB Memory, 1vCPU | 2GiB Memory, 2vCPU | 4GiB Memory, 4vCPU |
| Concurrent browsers allowed | Maximum of 10 browsers can be run concurrently | Maximum of 10 browsers can be run concurrently | Maximum of 10 browsers can be run concurrently | Maximum of 8 browsers can be run concurrently |
| Maximum number of Nodes that can be allotted | 10 | 10 | 5 | 2 |
| Maximum number of browsers allotted per node | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Maximum configuration possible | 10 nodes with 1 browser running in each node | 10 nodes with 1 browser running in each node | 5 nodes can be created with 2 browsers running in each node | 2 nodes can be created with 4 browsers running in each node |
-
The volume of requests being executed is not only related to its number or storage size of the requests. For example, you can have a million or more requests that do not take much time to be processed and executed, and all of them can be balanced with a processing power of 1GiB memory. Alternatively, you can have just a couple of requests that require a lot of time to process and require a processing power greater than that of 1GiB memory.
-
It is up to you to decide your Grid’s configuration based on the volume of your requests.
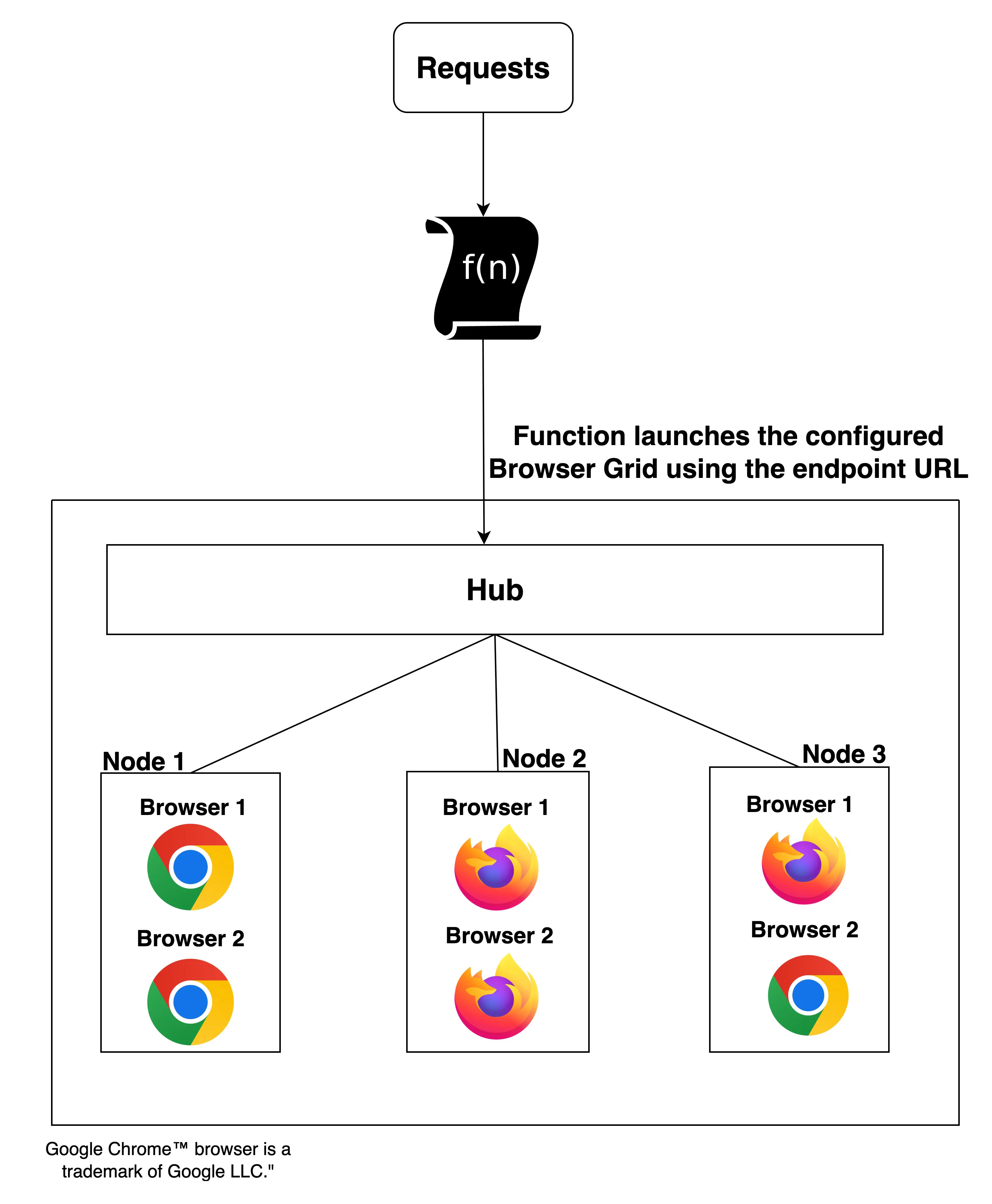
Hub-Node-Browser Relation
The following diagram illustrates the relation between hubs, nodes, and browsers.
Based on the volume of requests being sent, the hub will compute allocate nodes individually. When the first allotted node attains its maximum concurrency limit, with requests still pending, only then will the hub allot the next node.
These nodes will run the required headless browsers and process your requests. The number of nodes and browsers that are created by the hub will be based on the configuration you chose while creating your Browser Grid.
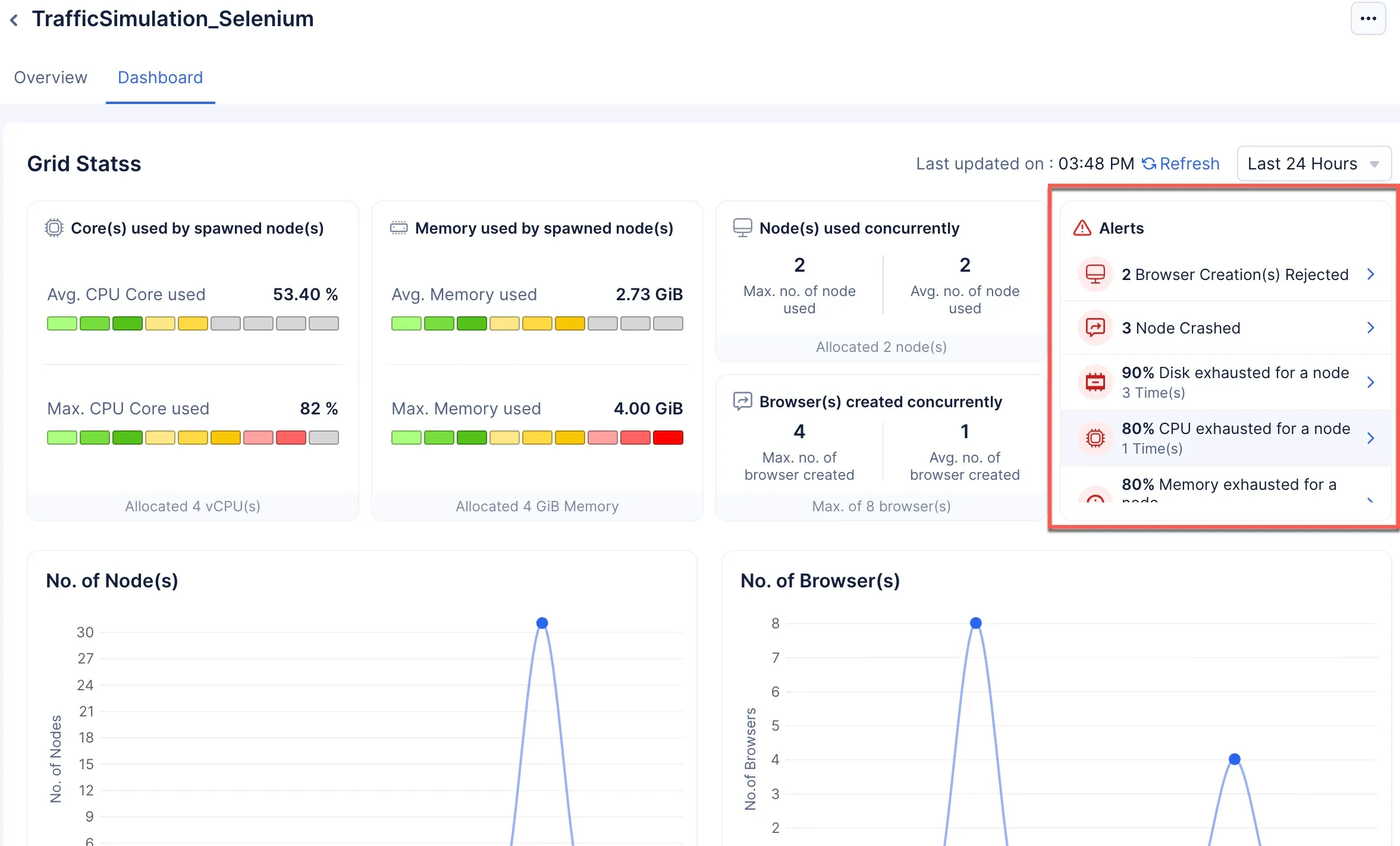
Alerts
Alerts is a feature in Browser Grid that will alert you to any error or configuration failure the grid encountered during its operations by populating the Alerts section in theDashboard.
The following are the five possible alerts that you may receive if your grid is not functioning as intended:
-
Browser Creation Rejected: This alert will be created if the grid is operating at maximum configuration, and you still have requests that need to be processed in the queue beyond the queue time (Selenium: 30 seconds, Puppetter/Playwright: 5 minutes). The queued requests demand new browsers be created, but none can be created as the configuration does not allow for it or there are no more browsers to be spawned, leaving the requests in the queue to be killed.
-
90% Disk Exhausted: This alert will occur if even one node’s allotted disk capacity has reached 90%. The default size allocated for the disk is 10GB.
-
80% Memory Exhausted: This alert will occur if even one node’s allotted memory is 80% consumed.
-
80% CPU Exhausted: This alert will occur if even one node reached 80% of the CPU capacity allotted to it.
-
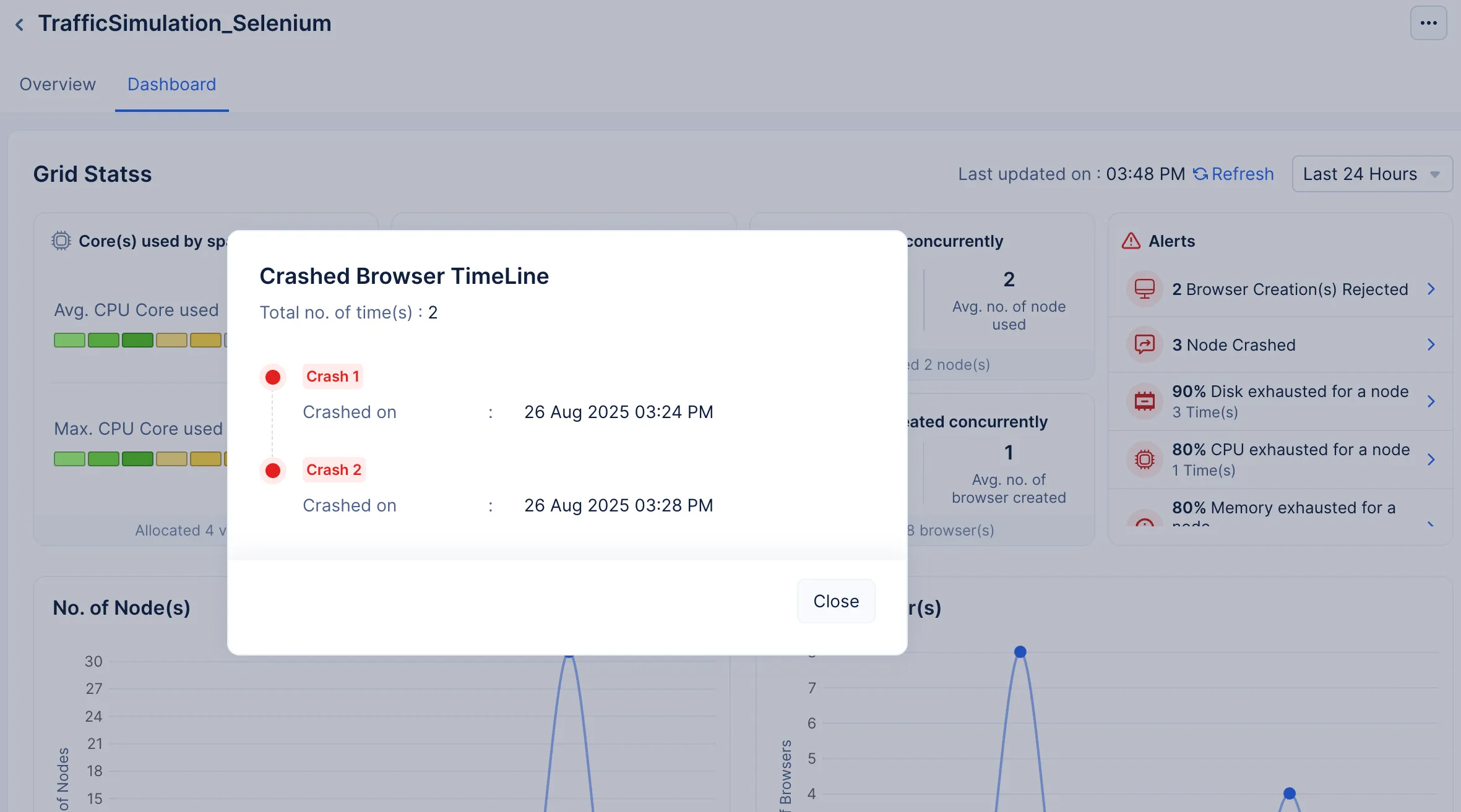
Nodes Crashed: This will only occur in severe times, when the node is operating at the maximum configuration allotted to it and is severely strained to process the volume of requests being sent to it.
You can click on a specific alert for more information about the alert notification.
To deal with these alerts:
- Try reducing the number of requests being sent for processing.
- Try updating the browser grid’s configuration.
Browser Grid States
-
Active: This is a state the Browser Grid enters into when you connect to the remote browser using its endpoint through code. While in this state, the browser grid spawns the required number of nodes and browsers to process the requests.
-
Inactive: This is a state the Browser Grid enters into when you stop the browser grid. This is the default the grid is in when you create a browser grid.
-
Idle: The Browser Grid is an auto-scaling component. Based on your demand, the required number of nodes and respective browsers are spawned (as per your configurations), and when there are no requests to be processed, the browsers and nodes are killed. Once the grid has scaled completely down and is not processing any requests, the browser grid will enter the Idle state. There will be no requests being processed in the grid.
Last Updated 2025-12-19 11:24:47 +0530 IST
Yes
No
Send your feedback to us