Deploy AppSail as a Custom Runtime from the CLI
Initialize or Add an AppSail Service
You can initialize an AppSail service for a custom runtime app directly in your app’s directory, or from a new directory using the Catalyst CLI. You can also add an AppSail service to an existing Catalyst project directory, where other resources have been initialized. You can deploy the AppSail service after you initialize or add it.
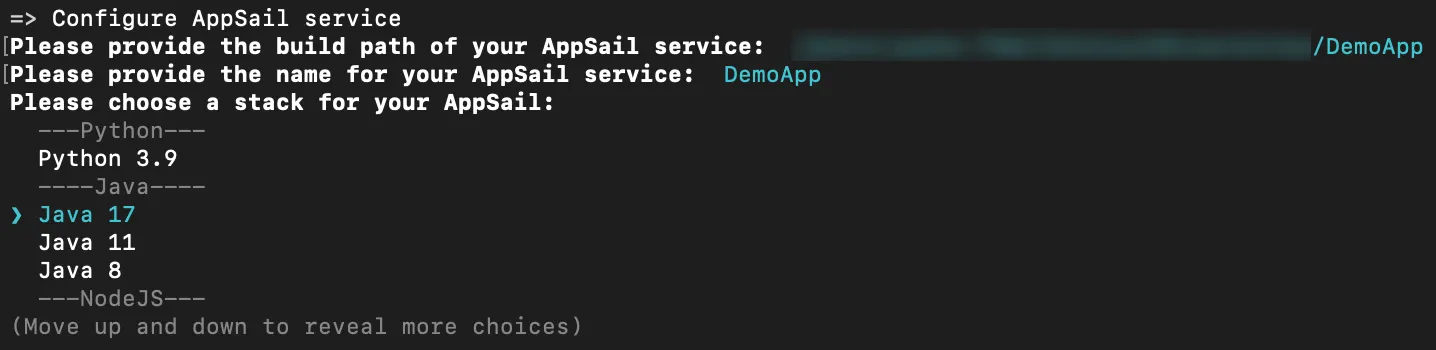
To initialize an AppSail service in a new directory, create a folder for your project in your local machine and navigate to it from your terminal. Initialize a project by executing the following command from that directory:
You can add an AppSail service in an existing Catalyst project directory by executing this CLI command:
Catalyst supports two protocols for custom runtime apps that you can use to associate your app’s image with AppSail. Each protocol has a distinct schema for identification and functioning.
-
Docker Image Protocol: Use this to associate a pre-built image of your app present in the local docker registry. The image must be built and tagged to point to the local registry. Example: docker://localhost/expres-hw:latest
-
Docker Archive Protocol: Use this to point to an archive file (.tar or .tar.gz) of a pre-built image of your app in your system’s directory. Example: docker-archive://test.tar
You need not provide any other details except the name for the AppSail for container images. The source or build path of the app, stack, and startup command are not required to be configured for OCI images, as they are already defined in the images. The steps to initialize or add the AppSail service will be the same as described below:
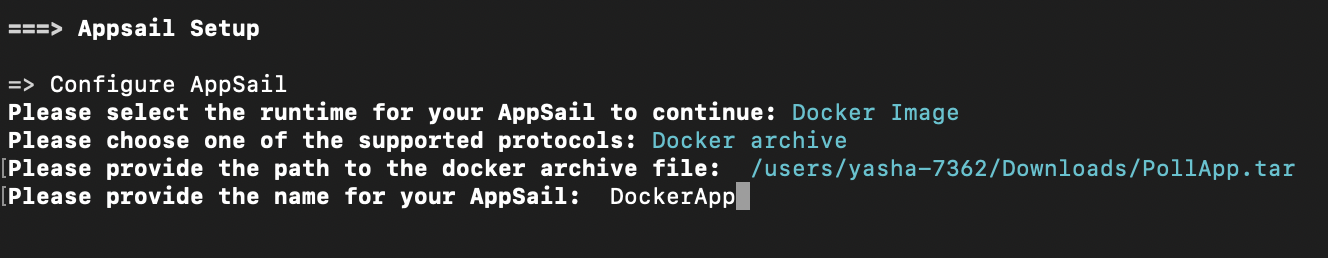
- The CLI will prompt you to select the runtime type as Catalyst-Managed Runtime or Docker Image when AppSail is initialized. Select the second option.
- Select the protocol as Docker Image or Docker Archive.
- Docker Image Protocol:
If you select Docker Image, the CLI will list all the available images with tags in the local docker registry. Select the image you need.
Docker Archive Protocol:
If you select Docker Archive, the CLI will prompt you to enter the absolute path to the TAR file image of your app in your local system.
- Provide a name for the AppSail service. You can name it anything you prefer.
AppSail is now initialized in your local directory, and the app’s image is now associated with the AppSail service. The configurations will be updated in catalyst.json file accordingly.
You can now code your business logic in your app, then serve the AppSail service through a localhost to debug and test it, or deploy it to the remote console directly.
Deploy an AppSail Service
Catalyst enables you to deploy AppSail services in two different ways:
-
Regular Deploy: The regular deploy execution applies when you have already initialized an AppSail resource either during the project initialization or by adding it in an existing project directory.
-
Standalone Deploy: You can do a standalone deploy of an app directly without initializing it as an AppSail service in prior.
The OCI image of your app that is associated with Appsail is deployed, along with the configuration file of your project.
Regular Deploy
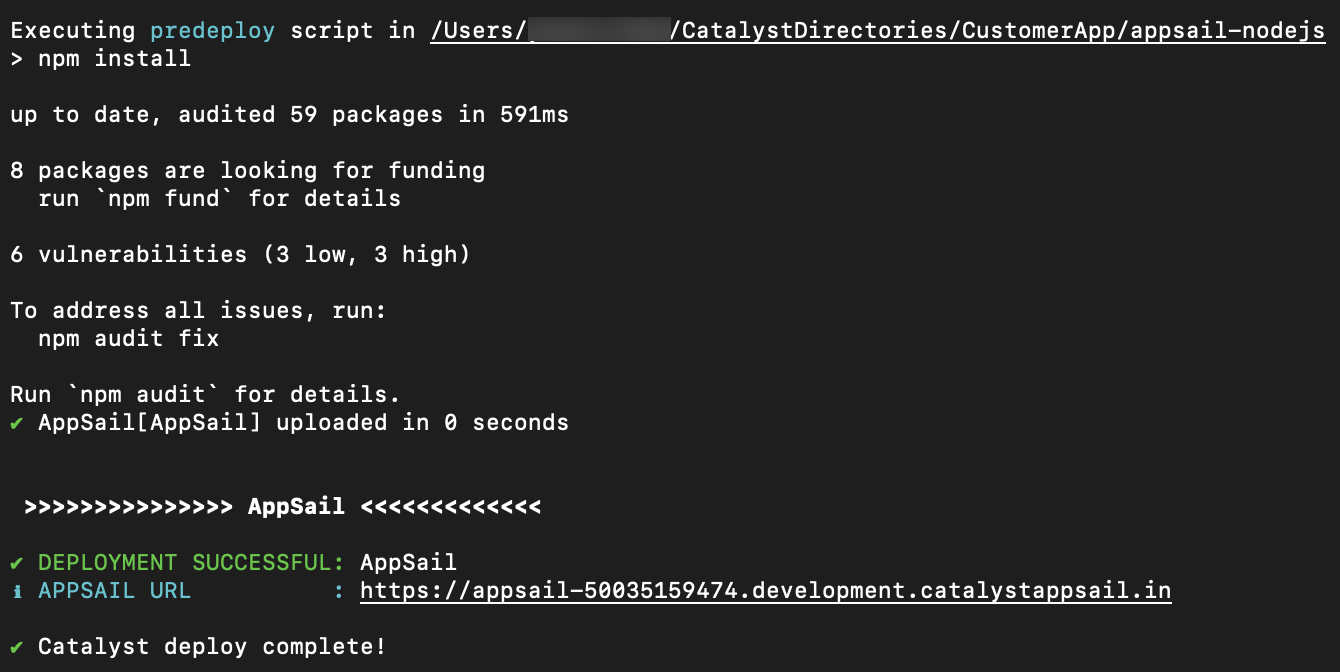
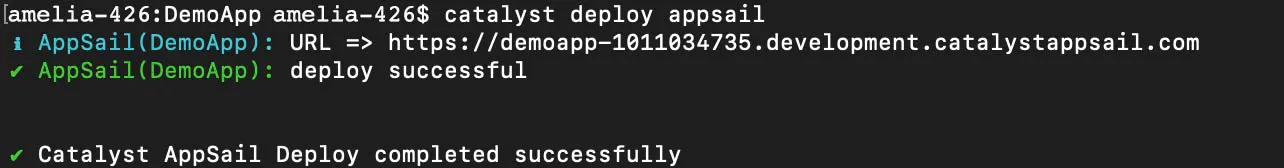
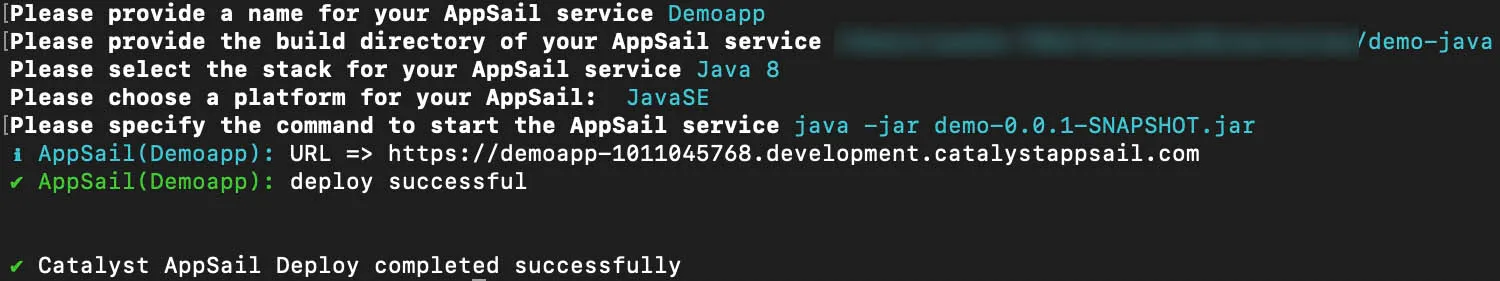
If the AppSail app is already initialized in the project directory, the CLI will automatically deploy the app with the rest of the project resources when you execute the catalyst deploy command. The CLI will display the endpoint URL of the app after it is deployed, that you can open it with.
If you have multiple AppSail apps in your project directory, you can access all of their URL endpoints from the CLI.
You can also execute the following command to deploy the AppSail service alone from your app’s source directory.
The deployment process is the same.
Standalone Deploy
You must execute the standalone deploy command from a Catalyst project directory’s root. That is, catalyst.json and other project dependency files must be present in the directory.
You can use the standalone deploy command with these options to deploy apps as container images: –name <name>, –source <image>, –command <command>, –port <port>. The first two are mandatory, while the last two are optional and can be used to override any startup commands or ports already configured in the container image definition. The options are explained in detail below.
You can do the standalone deploy of an AppSail app in the following way:
- Navigate to the directory the app’s deployable files are present in, and executing the following command:
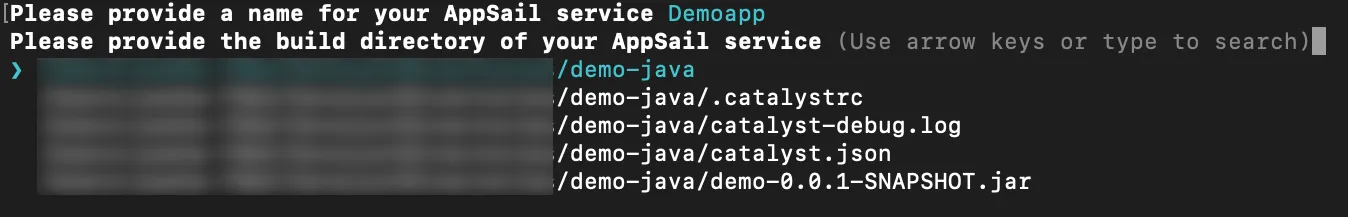
- Enter a name for your app. You can name the main file of your app’s build anything you prefer.
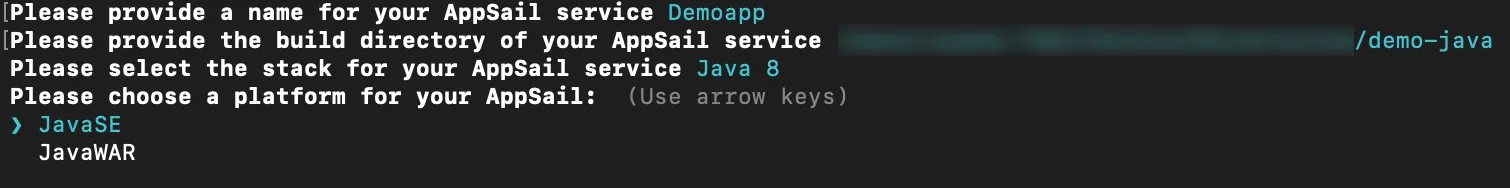
- Select the build path for your app from the list and press Enter.
- Select a stack for your app and press Enter.
If you select Java, the CLI will further prompt you to pick either Java SE or the Java WAR as your app’s deployable format.
If you select any other stack, this will be skipped.
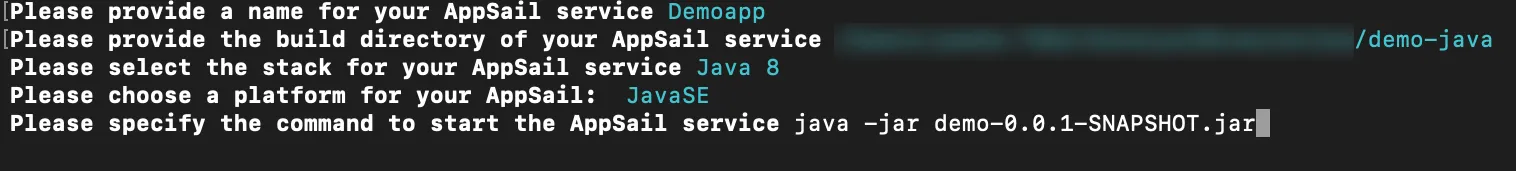
- You must additionally specify the startup command for your app based on the stack, framework, and web server used. This information will be directly deployed and will be available in the Configurations section of your console after the app deployment.
Your app is now directly deployed to the associated remote project without requiring you to initialize it as an AppSail resource. You can now access it with its endpoint URL displayed in the CLI.
Standalone Deploy AppSail Options
The catalyst deploy appsail standalone command supports the following options. Some of these are applicable to both Catalyst-managed runtime and container images apps, while some are specific to only one of them.
–name <name>
Use this to specify the name of your app. This is applicable to both Catalyst-managed runtime and container image apps. Example:
–command <command>
Use this to specify the startup command for your app. This is applicable to both Catalyst-managed runtime and container image apps. This will override any values already configured in the container image definition. Example:
–source <image>
Use this to specify the source of the docker image to be deployed. This is applicable only to container image apps. You must start with ‘docker://’ for Docker image protocol and ‘docker-archive://’ for Docker archive protocol. Refer here for details. Example:
–port <port>
Use this to specify the port for the AppSail. This is applicable only to container image apps. This will override any values already configured in the container image definition. Example:
Last Updated 2025-11-03 16:18:29 +0530 IST
Yes
No
Send your feedback to us