Key Concepts
In this section, we are going to go over some definitions and concepts about the Cron component to ensure you utilize cron effectively.
Cron Types
There are two types of cron: Pre-Defined Cron and Dynamic Cron. The following table illustrates their differences and their uses:
| Criteria | Pre-Defined Cron | Dynamic Cron |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | These crons are created and configured using the Builder feature present in the console. | These crons can also be configured using the Builder feature. However, since these crons are meant to be created dynamically during production runtime, the ideal practice is to create and configure these crons through code with the support of Catalyst SDKs in Java, Node.js and Python. |
| Primary advantage | You can create and configure these crons with no additional coding. These crons can be migrated to the Production environment, when you deploy your project. |
Since these crons are created dynamically during runtime, you can create and configure them using code. Greater flexibility to configure cron precisely to satisfy your requirement. |
| Primary restriction | Despite having multiple customization options, there could arise a possibility where you encounter minor restrictions in terms of precisely satisfying your requirement. For example, it is not possible for you to allow end-users to create your cron. The functionality of this type of cron is best suited for static purposes. |
Crons created in the Development environment will not be migrated to the Production environment when you deploy your project. |
| Cron Expression compatibility | The Builder provides you with format options that allow you to configure the schedule of these crons using Cron Expressions | Catalyst SDK supports the usage of Cron Expressions to define the schedule of the cron. |
| Ideal example use cases | Suitable for any type of use case, where you require a cron to schedule and periodically execute tasks on the assumption of preset conditions. Also suitable for use cases where you require the cron you created in development to be present during production. |
You can use this type of cron to satisfy any type of use case, where you require a particular action to occur at a particular time. Since these crons are created through code, it allows you to create crons with greater flexibility to employ versatile solutions. |
Cron ID
Cron ID is the unique ID generated by Catalyst when you create a Pre-defined or Dynamic cron.
Format Type
There are two format types you can use to configure your cron:
-
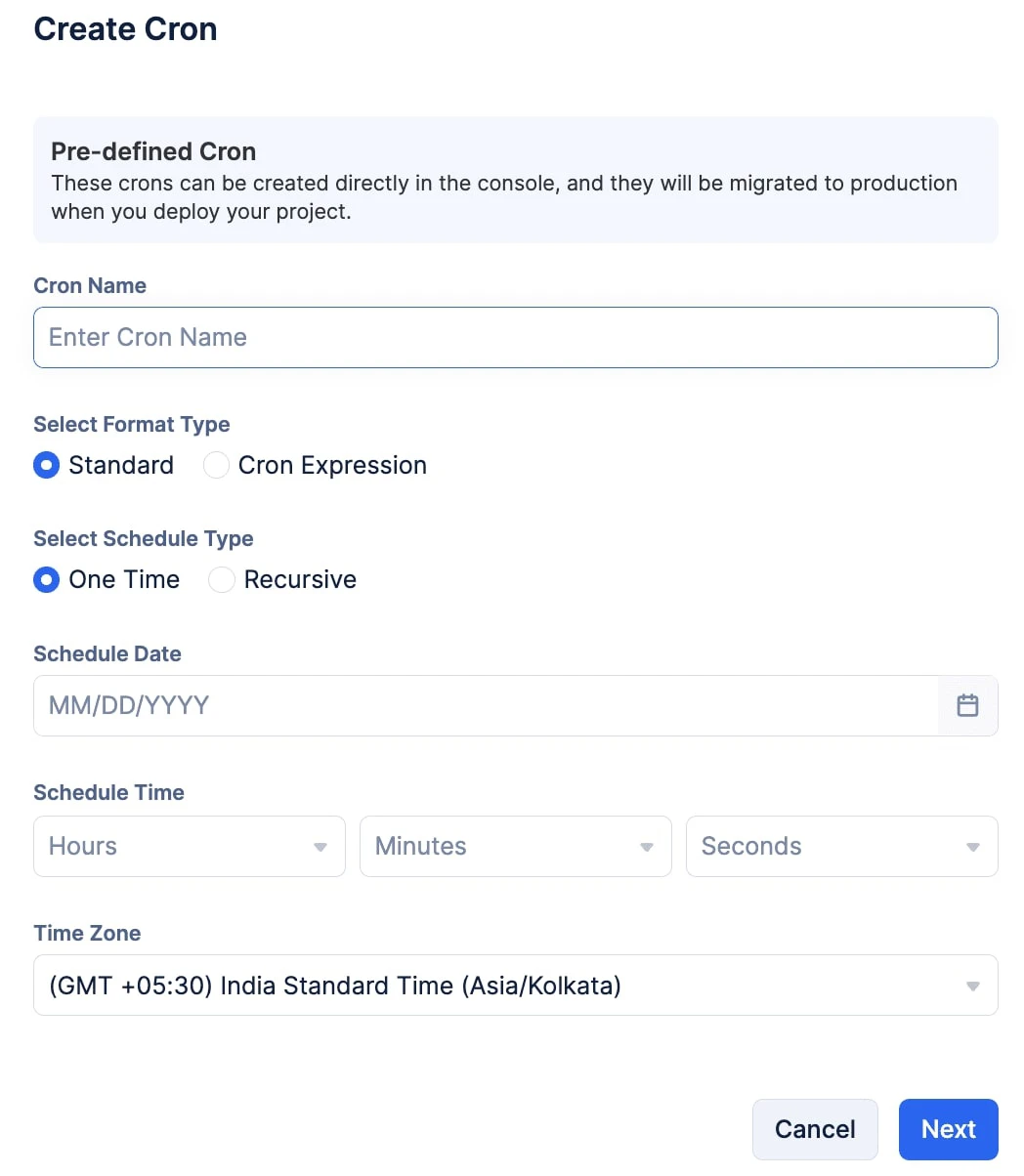
Standard: Standard is the format type to select if you prefer to use the UI Calendar-based options present in your builder to configure your cron.
-
Cron Expression: You use regex-like expressions to configure your cron. The expression allows you to configure cron in a quicker manner. Additionally, it allows you easily migrate crons you configured using other services to Job Scheduling’s Cron. Using cron expressions also provides you with more flexibility in configuring crons as you have greater input freedom.
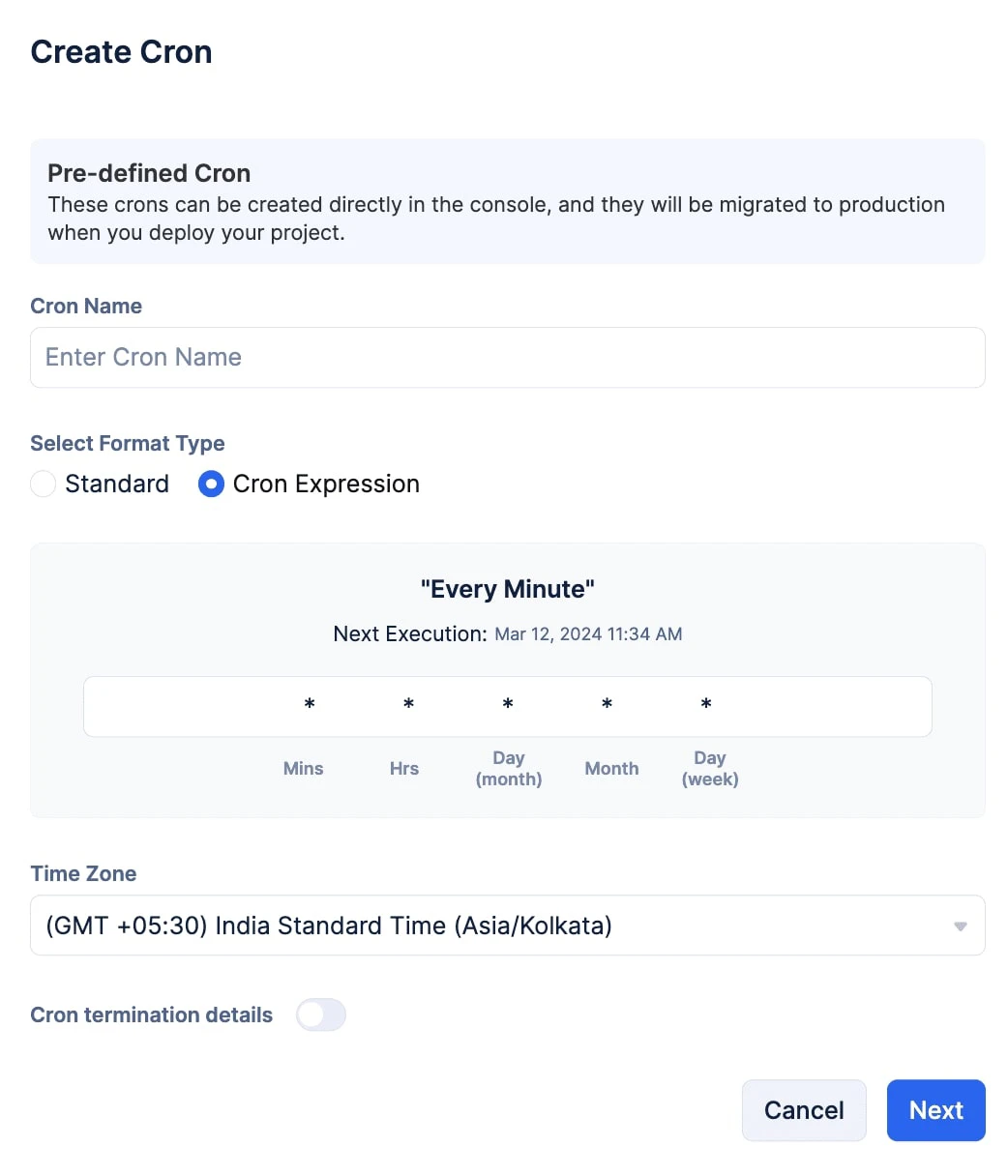
Cron Expressions
This is a format type you can choose to configure your cron. You can use these special expressions to provide five inputs to complete the configuration of your cron.
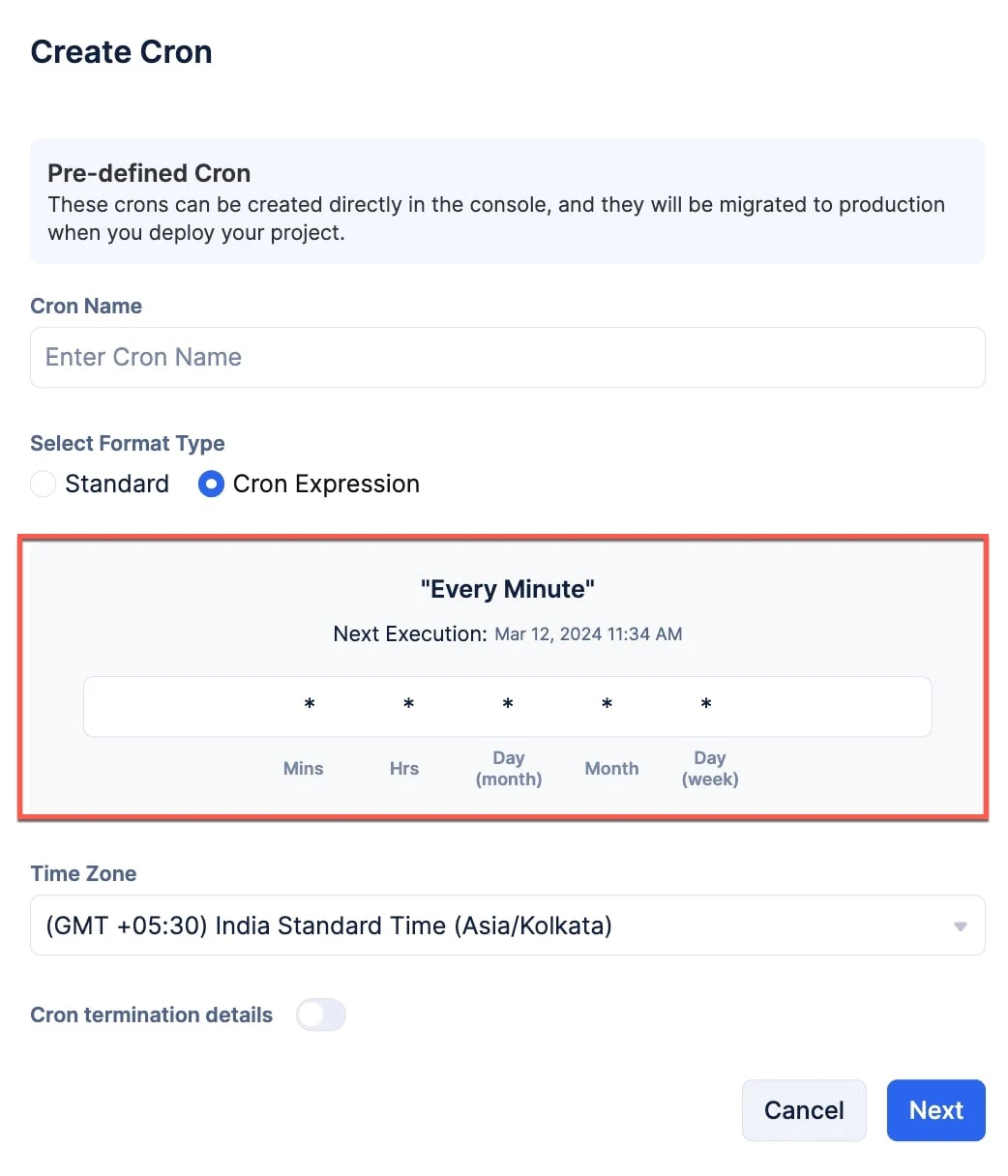
Study this section carefully to utilize Cron Expressions correctly.
Input fields present in cron expressions
| Input Fields | Meaning | Possible Values (Range) |
|---|---|---|
| Mins | Minutes of the clock | 0-59 |
| Hrs | Hours or the clock or the time in 24-Hr format | 0-23 |
| Day(Month) | Days of the calendar month | 1-31 |
| Month | Months present in a calendar year | 1-12 |
| Day(Week) | Days of the week | 0-6 (0/6 can be Sunday) |
Special characters present in Cron Expressions
| Special Characters | Meaning | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Asterisk (*) | All values | An asterisk under the Mins input field would mean "Every Minute" |
| Comma (,) | Used to denote specific values in a list of values | There is a list of seven days in a week. So, if 1,3,5 is inputted in the Days(Week) input field. The numbers and the comma would mean Monday, Wednesday, and Friday |
| Hyphen (-) | Used to denote the entire range of values in a list of values | If you input the value 1-3 in the Days(Week) input field. The expression would mean Monday through Wednesday. |
| Slash (/) | Used to denote repetitive increments of a value | If you input the expression 0/15 in the Mins input field. The expression would mean "Every 15 Minutes". |
| Hash (#) | Used to denote 'the nth day' of the week in the current month | If you input the expression 6#3 in the Days (Week) input field would mean "The 3rd Friday of the current month" |
Some examples of configuring crons using Cron Expressions
Example 1
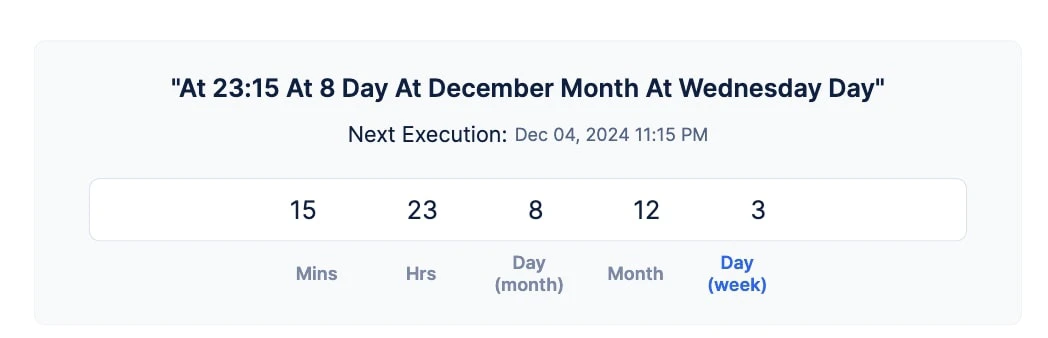
Requirement: Configure a cron to be executed on 8th Day of December of the current year at 11:15 PM.
Solution: Since it is a one-time cron, we don’t need to use special characters; just the number values would be sufficient. The expression would look like this:
Example 2
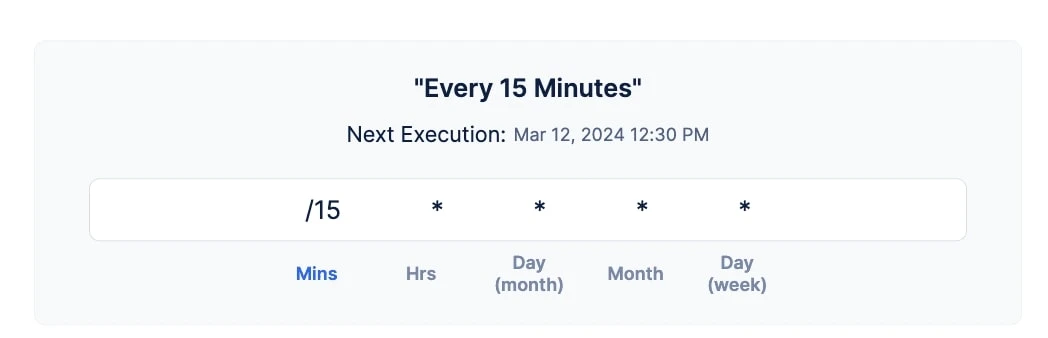
Requirement: Configure a recurring cron that should be executed every 15 minutes throughout the year of every year.
Solution: To achieve this cron, we will use the special character slash (/) cron expression, with the value 15 in the Mins input section.
Example 3
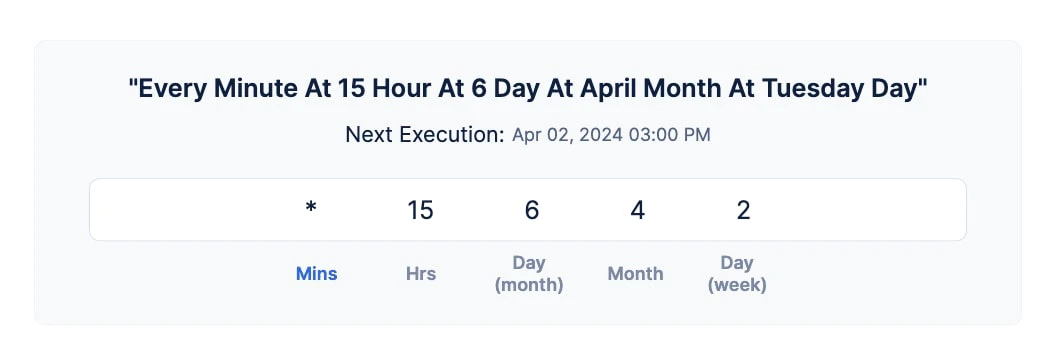
Requirement: Configure a recurring cron that should execute every minute of 3 PM on the 6th day of April if it falls on Tuesdays.
Solution: To achieve this cron, we will use the special character Asterisk (*) along with the appropriate field values.
Schedule Type
The schedule type determines the frequency of a cron submitting a job to the job pool. A cron can be scheduled in one of two ways:
- One Time: The cron schedules the job submission only once on the configured date and time.
- Recursive: The job submission by cron is triggered multiple times recursively based on the frequency, date, and time you configure. This functionality will continue till you disable or delete it, or provide a termination condition. The minimum recurring frequency a cron can be triggered at is one minute.
Last Updated 2025-10-08 19:32:16 +0530 IST
Yes
No
Send your feedback to us